Abstract
Background: Lenalidomide (LEN) is an oral mainstay of modern multiple myeloma (MM) treatment (given in 21day/7day (ON/OFF) cycles usually for 3-6 cycles). Non-adherence to oral anticancer therapy occurs in ~30% of cancer patients and is generally associated with adverse outcomes. Adherence to LEN in MM entails both adherence to duration of ON/OFF cycles as well as implementation adherence (defined as deviations from the dosing schedule while taking the drug (e.g., dosing/timing issues)). Data on adherence in MM is limited to retrospective pharmacy refill records showing 14.5% LEN implementation non-adherence (i.e., medication possession ratio <80%). There is no data on adherence to duration of LEN ON/OFF cycles. Electronic monitoring (EM) is the most reliable adherence measure to date, allowing assessment of both daily implementation adherence and duration of ON/OFF cycles
Aims: (1) To assess adherence to duration of LEN ON/OFF cycles; (2) To assess EM implementation adherence to LEN during ON cycles.
Methods: Using a prospective observational design including a convenience sample of LEN-naïve adult patients receiving LEN-based regimens for once-daily treatment of MM at 2 hematology centers in Israel (5/2016-11/2019).
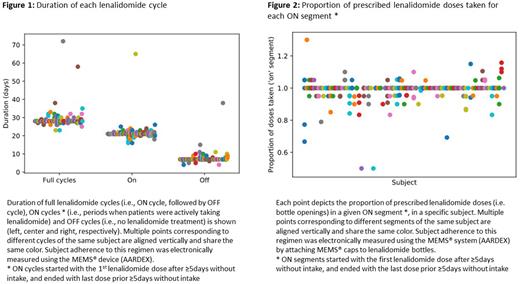
Adherence to ON/OFF cycle duration and implementation adherence was monitored using EM (MEMS®, AARDEX) for a maximum of 4 consecutive ON/OFF cycles. The MEMS® registers the date and time of each bottle opening as a proxy for LEN intake. Patients gave informed consent and were told about the EM adherence assessment. An ON cycle started with the first LEN dose after ≥ 5 days without intake and ended with the last dose prior ≥5 days without intake. OFF cycles were defined as periods between two ON cycles. The duration of ON/OFF cycles was expressed in days (median / IQR) and the proportion of patients adhering to ON/OFF cycles was calculated.
Implementation adherence during ON cycles was calculated twofold: (1) the proportion of days with any LEN intakes during ON cycles; (2) the proportion of prescribed drug taken was calculated (N-intakes/N-monitored-days). The number of patients with a proportion of days with intakes below 90% was calculated, since this cutoff was clinically relevant in a prior study of chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Descriptive statistics were calculated as appropriate.
Results: 85 of 93 patients enrolled were included in this analysis. Eight were excluded due to the inability to initiate use of the EM device and no patients were lost to follow-up. Sample characteristics are: 27 (32%) females; median age 68 years [IQR 60-74]; no. of pills/day, 5 [IQR 4-7]; prior disease duration, 19 months [IQR 5.75 - 45.7]; regimen: LEN-dexamethasone with (n=43, 51%) or without (n=38, 44%) additional drugs (5% missing); treatment line: 1st = 15%, 2nd = 66%, 3rd = 15% (4% missing). The median duration of follow-up was 133 days [IQR 77-152] and no. of cycles was 3 [IQR 1-4].
The median duration of ON/OFF cycles was 21 [21-21] and 7 [7-7] days, respectively (Figure 1). Adherence to ON/OFF cycle (21/7) duration was 75% (64/83). ON cycles shorter than 21 days were associated with a number of doses taken approximately equal to the duration of the cycle (e.g., duration = 20 days, median doses = 19). On the other hand, cycles longer than 21 days approximately corresponded to 21 doses taken, meaning that patients prolonged the ON cycle to make up for missed doses.
Median LEN implementation adherence was 99% [IQR: 97%-100%; range: 50%-100%]. Figure 2 shows the proportion of doses taken for each ON segment. All doses were taken by 43 patients (51%). One missed dose occurred in 18 (21%) subjects, two in 9 (11%), three in 7 (8%), and 8 (9%) had ≥4 missed doses, at any stage. Two or more consecutive doses were missed once in 8 patients (9%) and twice in 2 (2%). The proportion of days with intakes was below 90% in 4 patients (5%).
Conclusions: This study is the first to assess both adherence to LEN cycle duration and implementation adherence in patients with MM, using EM. 75% of patients fully adhered to the recommended 21-days-ON / 7-days-OFF cycles. LEN implementation adherence was high. Given that non-adherent patients are typically less willing to participate in EM a selection bias can not be excluded. While this data is somewhat reassuring, further research should determine which degree of deviation from the dosing schedule leads to adverse clinical outcomes.
Disclosures
Leader:Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Lectures; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Lectures; Sanofi: Other: Scientific lectures; Leo Pharma: Other: Lectures; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Lectures; Luzsana: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Pironet:AARDEX group: Current Employment. Tousset:AARDEX group: Current Employment. Raanani:BMS: Consultancy; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal